Last Updated on May 27, 2025 8:17:39 PM by Vivek Makwana
Learn how U.S. Treasury yields influence interest rates, mortgage loans, and investment returns in 2025. A clear, beginner-friendly guide for smart financial decisions.
U.S. Treasury yields might sound like something only economists care about, but they play a powerful role in everyday financial life. From the interest rate on your mortgage to the returns on your investment portfolio, Treasury yields act as a key indicator of where the economy is headed. In 2025, with market uncertainty and evolving Federal Reserve policies, understanding how these yields work is more important than ever. In this guide, we’ll break down what Treasury yields are, how they influence interest rates and loans, and what they mean for investors like you.
What Are U.S. Treasury Yields?
Treasury yields represent the return you earn when you invest in U.S. government bonds. These bonds are considered one of the safest investments in the world, backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
Each type of bond—2-year, 10-year, 30-year—has its own yield, and these yields fluctuate daily based on supply, demand, inflation expectations, and monetary policy.
In simple terms:
When demand for Treasuries goes up, prices rise and yields go down.
When demand falls, prices drop and yields rise.
How Treasury Yields Affect Interest Rates
One of the most direct ways Treasury yields impact your life is through interest rates. While the Federal Reserve sets the short-term federal funds rate, longer-term interest rates are heavily influenced by Treasury yields, especially the 10-year yield.
Here’s how it works:
Mortgage rates often follow the 10-year Treasury yield.
Auto loans, personal loans, and credit card rates are also influenced by Treasury yield trends.
As Treasury yields go up, borrowing becomes more expensive. As they go down, loans become cheaper.
Example (2025): If the 10-year Treasury yield rises to 5%, mortgage rates may climb above 7%, making home ownership more expensive.
Why Do Treasury Yields Rise or Fall?
Several key factors influence Treasury yields:
- Federal Reserve Policy – When the Fed raises interest rates, short-term Treasury yields usually rise.
- Inflation Expectations – Higher expected inflation reduces the real return on bonds, pushing yields higher.
- Investor Sentiment – In times of economic uncertainty, investors flock to Treasuries, driving yields down.
- Global Events – Wars, oil prices, and international market trends can shift bond demand.
Impact on Mortgage Loans and Consumer Borrowing
When Treasury yields rise, banks have to pay more to borrow money, and they pass that cost on to consumers. This means:
Higher mortgage rates
Increased loan payments
Slower housing market activity
In 2025, with inflation still being closely monitored, the Fed’s stance and the yield curve have created more cautious lending conditions. If you’re looking to refinance or take out a loan, tracking Treasury yields can help you time it better.
What Treasury Yields Mean for Investments
Treasury yields also serve as a benchmark for many investment decisions.
Here’s how:
Higher yields make bonds more attractive, possibly pulling money out of the stock market.
Lower yields can drive investors to riskier assets like stocks, real estate, or crypto.
They influence corporate borrowing costs, which affects company profits and stock valuations.
Treasury yields also play a role in determining dividend yield comparisons.
Investor Tip (2025): If 10-year Treasuries yield 4.8%, and your favorite dividend stock only pays 3%, you might reconsider your portfolio balance.
As of May 15, 2025, the U.S. 10-year Treasury yield is approximately 4.54%.
This yield has been on an upward trend recently, influenced by factors such as declining inflation and steady Federal Reserve policies. Notably, the real (inflation-adjusted) yield on the 10-year Treasury is nearing 2.20%, the highest in a decade, effectively tightening financial conditions.
The official source for U.S. Treasury yield data is the U.S. Department of the Treasury. You can find up-to-date and historical yield information directly from their website:
Official Website:
The correct and official source for U.S. Treasury yield data is the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Interest Rate Statistics page.
You can access it here:
🔗 Interest Rate Statistics | U.S. Department of the Treasury
This page provides comprehensive information on daily Treasury yield curve rates, including par yield curves for various maturities. It’s an authoritative resource for up-to-date and historical yield data.
Here is the image of the U.S. Treasury yield curves chart
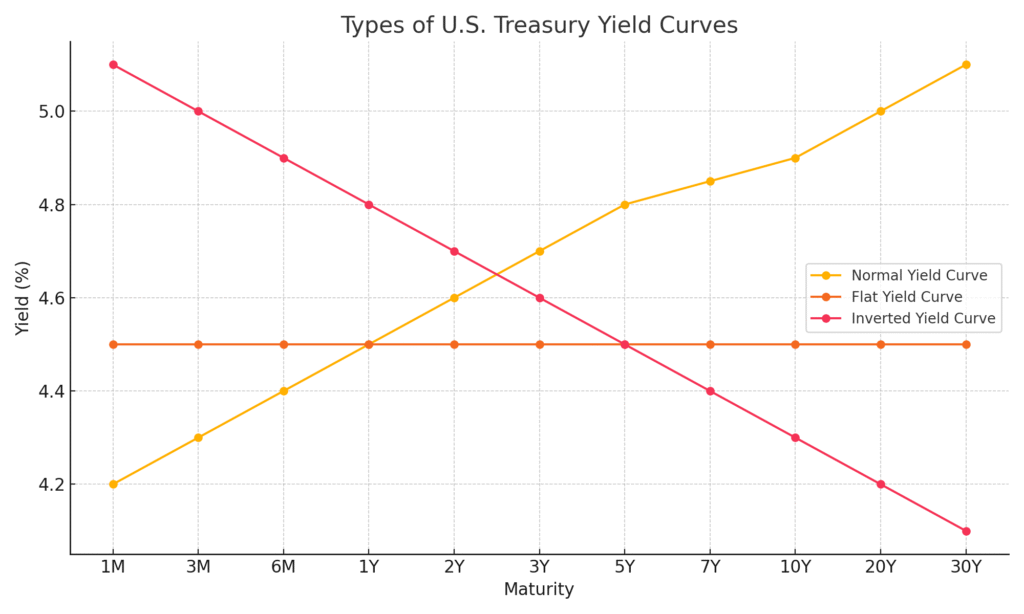
Normal Curve: Yields increase with longer maturities (sign of growth).
Flat Curve: Yields are nearly the same across all terms (economic uncertainty).
Inverted Curve: Short-term yields are higher than long-term (possible recession signal).
Final Thoughts: Why It All Matters
Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, investing for retirement, or simply keeping an eye on economic trends, U.S. Treasury yields are a crucial piece of the puzzle. They act like a financial thermometer—showing where money is flowing, how much borrowing will cost, and how attractive different investments are.
In 2025, staying informed about Treasury yield trends can help you make smarter financial choices—especially in a market still adjusting to post-pandemic and inflation-driven shifts.
Looking to stay updated on Treasury yields and financial trends?
Bookmark paisokagyan.com for more insights and practical advice.


